[javascript] 프로토타입
코어 자바스크립트 책에 있는 내용과 예제를 요약한 포스트입니다.
클래스 기반 언어 : 상속을 사용함.
프로토타입 기반 언어 : 객체를 원형(prototype)으로 삼고 참조함으로써 상속과 비슷한 효과를 얻음.
1. 프로토 타입의 개념 이해
1.1. construtor, prototype, instance
var instance = new Contructor();
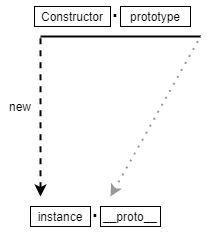
- 생성자 함수
Contructor를new와 함께 호출 Constructor에서 정의된 내용을 바탕으로 새로운instance가 생성- 이 때 instance에는
__proto__프로퍼티가 자동으로 부여되는데 __proto__는Contructor의prototype이라는 프로퍼티를 참조
prototype 객체 내부에는 인스턴스가 사용할 메서드를 저장하며,
인스턴스에서 이를 참조하는 __proto__ 를 통해 이 메서드에 대해 접근할 수 있게 된다.
[참고] 실제로 __proto__에 접근할 때는, Object.getPrototypeOf() / Object.create()등을 이용한다.
var Person = function(name){
this._name = name;
};
Person.prototype.getName = function(){
return this._name;
};
var suzi = new Person('Suzi');
suzi.__proto__.getName(); // undefined
Person.prototype === suzi.__proto__ // true
- proto 객체에 name 프로퍼티가 있는 경우
var suzi = new Person('suzi');
suzi.__proto__.name = 'SUZI_proto__';
suzi.__proto__.getName(); // SUZI_proto__
this가 인스턴스를 가리키게 하고싶으면 바로 메서드를 쓰면 된다. ->__proto__는 생략 가능한 프로퍼티이기 떄문에 가능하다.
var suzi = new Person('Suzi');
suzi.getName(); // Suzi
var iu = new Person('Jieun');
iu.getName(); // Jieun
// __proto__를 생략.
- 크롬 개발자도구 콘솔창에서 디렉터리 구조 확인하기
var Constructor = function(name){
this.name = name;
};
Constructor.prototype.method1 = function(){};
Constructor.prototype.property1 = 'Constructor Prototype Property';
var instance = new Constructor('Instance');
console.dir(Constructor); // f Contructor(name)
console.dir(instance); // Const
콘솔창에서 Constructor의 prototype를 확인하면, method1, property1등의 값이 보인다. instance의 디렉터리 구조를 확인하면 __proto__가 Constructor의 prototype과 동일한 내용으로 구성되어있음을 확인할 수 있다.
1.2. constructor 프로퍼티
생성자 함수의 프로퍼티인 prototype 객체 내부에는 constructor 프로퍼티가 있다. (인스턴스의 __proto__ 내부도 마찬가지)
이 프로퍼티는 원래의 생성자 함수인 자기 자신을 참조한다.
var arr = [1, 2];
Array.prototype.constructor === Array; // true
arr.__proto__.constructor === Array; // true
arr.constructor === Array; // true
var arr2 = new arr.constructor(3, 4);
console.log(arr2); // [3, 4]
6번째줄 코드를 보면 __proto__가 생략되어 인스턴스에서 직접 constructor에 접근할 수 있기 때문에
오류 없이 동작할 수 있다.
읽기 전용 속성이 부여된 리터럴 변수 number, string, boolean 등을 제외하고는
constructor를 사용하여 값을 바꿀 수 있다.
var NewConstructor = function(){
console.log('this is new constructor!');
};
var dataTypes = [
1, // Number & false
'test', // String & false
true, // Boolean & false
{}, // NewConstructor & false
[], // NewConstructor & false
function(){}, // NewConstructor & false
/test/, // NewConstructor & false
new Number(), // NewConstructor & false
new String(), // NewConstructor & false
new Boolean, // NewConstructor & false
new Object(), // NewConstructor & false
new Array(), // NewConstructor & false
new Function(), // NewConstructor & false
new RegExp(), // NewConstructor & false
new Date(), // NewConstructor & false
new Error() // NewConstructor & false
];
dataTypes.forEach(function(d){
d.constructor = NewConstructor;
console.log(d.constructor.name, '&', d instanceof NewConstructor);
});
모든 데이터가 d instance of NewConstructor 명령에 대해 false를 반환한다.
constructor를 변경하더라도 참조하는 대상이 변경될 뿐, 인스턴스의 원형이 바뀌거나 데이터타입이 변하지는 않는 다는 점을 통해
인스턴스의 생성자 정보를 알기 위해 constructor 프로퍼티에 의존하는 것은 안전하지 않다는 점에 유의하도록 하자.
(그러나 이를 통해 클래스 상속을 흉내내는 것이 가능하다. - 7장 참고)
- 다양한 conctructor 접근 방법
var Person = function(name) {
this.name = name;
};
var p1 = new Person('사람1'); // { name: '사람1' } true
var p1Proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(p1);
var p2 = new Person.prototype.constructor('사람2'); // { name: '사람2' } true
var p3 = new p1Proto.constructor('사람3'); // { name: '사람3' } true
var p4 = new p1.__proto__.constructor('사람4'); // { name: '사람4' } true
var p5 = new p1.constructor('사람5'); // { name: '사람5' } true
[p1, p2, p3, p4, p5].forEach(function(p){
console.log(p, p instance of Person);
});
p1 ~ p5 는 전부 Person의 인스턴스다.
- 동일한 대상을 가리킴
[Contructor] [instance].__proto__.constructor [instance].constructor Object.getPrototypeOf([instance]).constructor [Constructor].prototype.constructor - 동일한 객체(prototype)에 접근할 수 있음
[Contructor].prototype [instance].__proto__ [instance] Object.getPrototypeOf([instance])
2. 프토로타입 체인
2.1. 메서드 오버라이드
prototype 객체를 참조하는 __proto__는 생략이 가능하여
인스턴스는 prototype에 정의된 프로퍼티나 메서드를 자신의 것처럼 사용할 수 있다.
이 때 인스턴스가 동일한 이름의 프로퍼티나 메서드를 가지고 있다면 어떨지 확인해보자.
- 메서드 오버라이드 ```javascript var Person = function(name){ this.name = name; }; Person.prototype.getName = function(){ return this.name; };
var iu = new Person(‘지금’); iu.getName = function(){ return ‘바로 ‘ + this.name; }; console.log(iu.getName()); // 바로 지금
위 예제를 확인하면 메서드 오버라이드가 일어나고 있다.
자바스크립트 엔진이 `getName` 메서드를 찾을 때 자신의 프로퍼티를 검색하고
없을 경우 `__proto__`를 검색하기 때문에 검색순서에서 밀릴 뿐 원본이 교체되는 것이 아닌 덮어씌우는 개념이라고 이해하면된다.
이 때 `prototype`에 있는 원본 메서드에 접근하려면 다음과 같이 하면 된다.
```javascript
console.log(iu.__proto__.getName()); // undefined
Person.prototype.name = '이지금';
console.log(iu.__proto__.getName()); // 이지금 // this: Person.prototype
console.log(iu.__proto__.getName.call(iu);) // 지금 // this: iu (instance)
2.2. 프로토타입 체인
console.dir({a : 1});
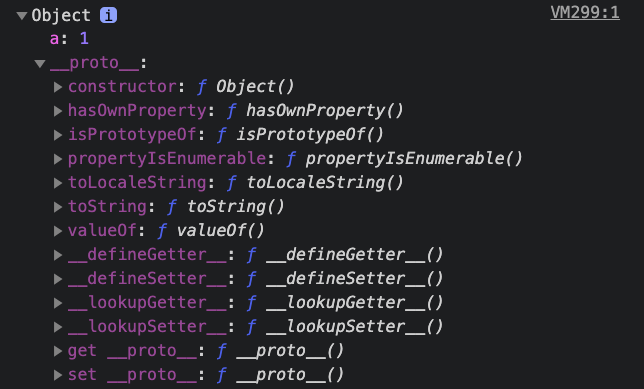
객체 내부 구조를 확인 해보면,
프로퍼티의 값이 있고 __proto__ 내부에 hasOwnProperty, isPrototypeOf, toLocaleString, toString, valueOf 등 메서가 있으며
constructor는 생성자 함수인 Object를 가리키고있다.
이어서 배열의 내부구조를 콘솔을 통해 확인해보면,
__proto__에는 pop, push...등 배열메서드와 Array를 가리키고 있는 constructor가 있고
__proto__의 내부의 __proto__는 위 그림과 같이 객체의 __proto__와 동일한 내용으로 이루어져있다.
이는 prototype객체가 Object이기 때문이다. 기본적으로 모든 객체의 __proto__는 Object.prototype과 연결된다.
var arr = [1, 2];
arr.push(3); // arr.__proto__.push(3);
// [1, 2, 3]
arr.hasOwnProperty(2); // arr.__proto__.__proto__.hasOwnProperty(2);
// true
__proto__는 생략이 가능하며, 생략 가능한 __proto__를 한번 더 탐색하면
Object.prototype을 참조할 수 있기 때문에 위의 실행이 가능하다.
이를 프로토타입 체인(prototype chain)이라 하며, 이 체인을 따라 검색하는 것을 프로토타입 체이닝(prototype chaining)이라 한다.
- 메서드 오버라이드와 프로토타입 체이닝 ```javascript var arr = [1, 2]; Array.prototype.toString.call(arr); // 1, 2 Object.prototype.toString.call(arr); // [object Array] arr.toString(); // arr.proto.toString // 1, 2
arr.toString = function(){ return this.join(‘_’); } arr.toString(); // arr.toString // 1_2
## 2.3. 객체전용 메서드의 예외사항
`Object.prototype`은 언제나 프로토타입 체인의 최상단에 존재한다.
따라서 객체에서만 사용할 메서드는 프로토타입 객체 안에 정의할 수 없다. 당연한 이야기인게, 객체만 사용할 메서드인데 `Object.prototype`에 정의하면 다른 데이터 타입도 해당 메서드를 사용할 수 있게되기 때문이다.
- **Object.prototype에 추가한 메서드에 접근**
```javascript
Object.prototype.getEntries = function(){
var res =[];
for(var prop in this){
if(this.hasOwnProperty(prop)){
res.push([prop, this[prop]]);
}
}
return res;
};
var data = [
['object', {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}], // [["a", 1], ["b", 2], ["c", 3]]
['number', 345], // []
['string', 'abc'], // [["0", "a"], ["1", "b"], ["3", "c"]]
['boolean', false], // []
['func', function(){}], // []
['array', [1, 2, 3]], // [["0", 1], ["1", 2], ["2", 3]]
];
data.forEach(function(datum){
console.log(datum[1].getEntries());
});
예제에서 객체에서만 사용할 의도로 getEntries 메서드를 만들었으나,
실행 시 모든 데이터가 오류 없이 결과를 반환하고 있다.
어떤 데이터 타입이건 프로토타입 체이닝을 통해 getEntries에 접근할 수 있어 그렇다.
그래서 객체만을 대상으로 동작하는 객체전용 메서드들은 Object.prototype이 아닌 Object내에 static method로 부여할 수 밖에 없다.
이게 무슨 말이냐면… 객체 전용 메서드를 호출할때
instance.freeze()로 표현하지 않고 Object.freeze(instance) 식으로 호출되는 것이다.
반대로 모든 데이터에서 활용할 수 있는 범용적인 메서드인
toString, hasOwnProperty, valueOf, isPrototypeOf는 모든 변수가 자신의 메서드인 것 처럼 호출할 수 있다.
[참고] Object.create
프로토타입 체인 상 가장 마지막에는 언제나 Object.prototype이 있으나,
예외적으로 Object.create(null)을 사용하면 __proto__가 없는 객체를 생성한다.
var _proto = Object.create(null);
_proto.getValue = function(key){
return this[key];
};
var obj = Object.create(_proto);
obj.a = 1;
console.log(obj.getValue('a')); // 1
console.dir(obj); // __proto__에 getValue()만이 존재함.
예제를 확인해보면, _proto에 proto 프로퍼티가 없는 객체를 할당하고, obj는 _proto를 proto 로 갖는 객체를 할당했다.
마지막 라인을 확인해보면 __proto__에 getValue 메서드만이 존재하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이를 통해 내장 메서드와 프로퍼티가 제거되어 기능에 제약이 생기나 객체 자체의 무게가 가벼워져 성능상 이점을 가진다.
2.4. 다중 프로토타입 체인
var Grade = function(){
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); // [100, 80]
for(var i = 0; i < args.length; i++){
this[i] = args[i];
}
this.length = args.length;
};
var g = new Grade(100, 80);
변수 g 는 Grade의 인스턴스를 바라본다.
Grade의 인스턴스는 인자를 받아 배열형태로 저장한 유사배열 객체이며, 배열 메서드를 사용할 수 없다.
인스턴스에서 바로 배열 메서드를 직접쓸 수 있게 하고싶을 때, g.__proto__, 즉 Grade.prototype이 배열의 인스턴스를 바라보게 하면 된다.
Grade.prototype = [];
이렇게 체인을 연결하면 g인스턴스에서 직접 배열 메서드를 사용할 수 있으며,
이 인스턴스에서는 g객체 자체가 지니는 멤버, Grade의 prototype에 있는 멤버, Array.prototype, Object.prototype에 있는 멤버까지 접근할 수 있게되며
이렇게 두 단계 이상의 체인을 지니는 다중 프로토타입 체인도 가능하다는 점을 확인하고 넘어가자.
3. 정리
- 생성자 함수를
new와 함께 호출하면,Constructor에서 정의된 내용을 바탕으로 새로운 인스턴스가 생성되며, 인스턴스에는Constructor.prototype을 참조하는__proto__프로퍼티가 자동으로 부여된다. __proto__는 생략이 가능하므로 인스턴스는Constructor.prototype의 메서드를 자신의 메서드처럼 호출 할 수 있다.Constructor.prototype에는contructor프로퍼티가 있으며 이는 생성자 함수 자신을 가리킨다.__proto__의 최상위에는Object.prototype이 있다. 이를 탐색하는 과정을 프로토타입 체이닝이라 한다.- 프로토타입 체이닝을 통해 각 상위 프로토타입의 메서드를 자신의 것처럼 호출할 수 있다.
Object.prototype에는 모든 데이터 타입에서 사용할 수 있는 범용 메서드만 존재하며, 객체 전용은Object생성자 함수에static으로 존재한다.- 프로토타입 체인은 두 단계 이상의 체인을 지닐 수 있다.

Comments